Blockland
Setup
Pre-requisite
Before you are able to setup a demo of blockland, you will need to:
- Setup a linux machine and have access to root user (Be root user when running one-liner). with atleast 512 mb of ram.
- Machine has to have git installed, if not use this command:
sudo apt-get install git-all(Most debian distros have git installed for the box)
One-line setup
To install and setup blockland type in this command in a bash terminal (Read Pre-requisite)
wget -O - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DanielHauge/BlockLand/master/SetupBlockLand.sh | bash
Runs that are tested and works:
- We have tested with a digital ocean droplet of 512mb size, which works.
- We have tested on a ubuntu 16.04 vagrant image.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "bento/ubuntu-16.04"
config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 8888, host: 8888, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.11"
config.vm.define "Linux", primary: true do |dockermachine|
dockermachine.vm.hostname = "Linux"
dockermachine.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
sudo echo "Ready at 192.168.33.11"
SHELL
end
end
- We have also tested with a debian vagrant image hat works:
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "debian/jessie64"
config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 8888, host: 8888, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.13"
config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/home/vagrant/sync", disabled: true
config.vm.define "Linux", primary: true do |dockermachine|
dockermachine.vm.hostname = "Linux"
dockermachine.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
sudo echo "Ready at 192.168.33.13"
SHELL
end
end
Documentation
Test run video
Click me!
The Idea behind our Blockhain Implementation
Our idea for the Blockchain is to create verifications for a housing queue. In big cities there is often a shortage of apartments and people usually need to stand in queue for several years to be able to get a lease. There is a risk that people having access to the queueing system might manipulate the queue, something that has been reported in the news papers from time to time. Those standing in the housing queue want to be insured that the queue is not manipulated. We have implemented a democratic system with the help of Blockchain technology guarantees that the queue can not be manipulated. We also use a council algorithm ensures that it is time when the request to make a transaction like signing up for the queue and not mining speed that is the determiner factor for who gets to do the transaction first.
A Brief Technical Description
We have written the Blockchain program in Go. We use the following technologies to set up the program, Go lang, Docker, Docker Compose and a Linux machine. In this documentation we will only link to PeerToPeer software however the PeerToPeerSlow works in the same way.
Architecture
Our BlockChain program runs on a network of distributed nodes. It uses a peer to peer architecture consisting of peers that are equal. A Peer is also referred as a node in the program and documentation. Each peer runs on a docker container. The Peers communicate via TCP as a network protocol and JSON is used as the data exchange format. Each peer runs the BlockChain software and has a API endpoint. The API endpoint is used to trigger actions and BlockChain transactions.
BlockChain - Implemented actions
-
Connect to Peer to Peer network. The peers (nodes) are instantiated with a docker-compose.yml. It uses the Docker image build with the dockerfile. The arguments for the docker image can be found in the docker-compose file under
entrypoint: ./go 127.0.0.1 Daniel :8080. -
Disconnect to Peer to Peer network. - This functionality is implemented but not used.
BlockChain Transactions
Mining of Blocks (Concensus of algorithm)
We are using the Hash algorithm of Sha256. Which is pretty standard in most cases. For the proof of work we are using nonce that give six zeros in the beginning of the hash.
hash = sha256.Sum256(data)
Council style instead of Anarchy
Bitcoin always rewards the fastest miner, this allows for complete independence for all miners, but this setup is full anarchy. Issue is for our project if we had several equally fast miners, all mining at the same time that then presented when they were ready, they would invalidate the others work whenever the current block was mined, resulting in wasted resources.
We choose to run a council style setup, that follows the Independence style for mining, but instead of everyone wasting their time mining at the same time, one will ask for a council meeting, and depending on the council meeting que, will either start one or wait till it becomes that miners turn. This way the system doesn’t care about who’s faster, although it’s not a practical system for large scale since one miner mines while 1 million others wait, but for a small scale project it’s a very efficient way, and allows for structual fairness and further control of the blockchain.
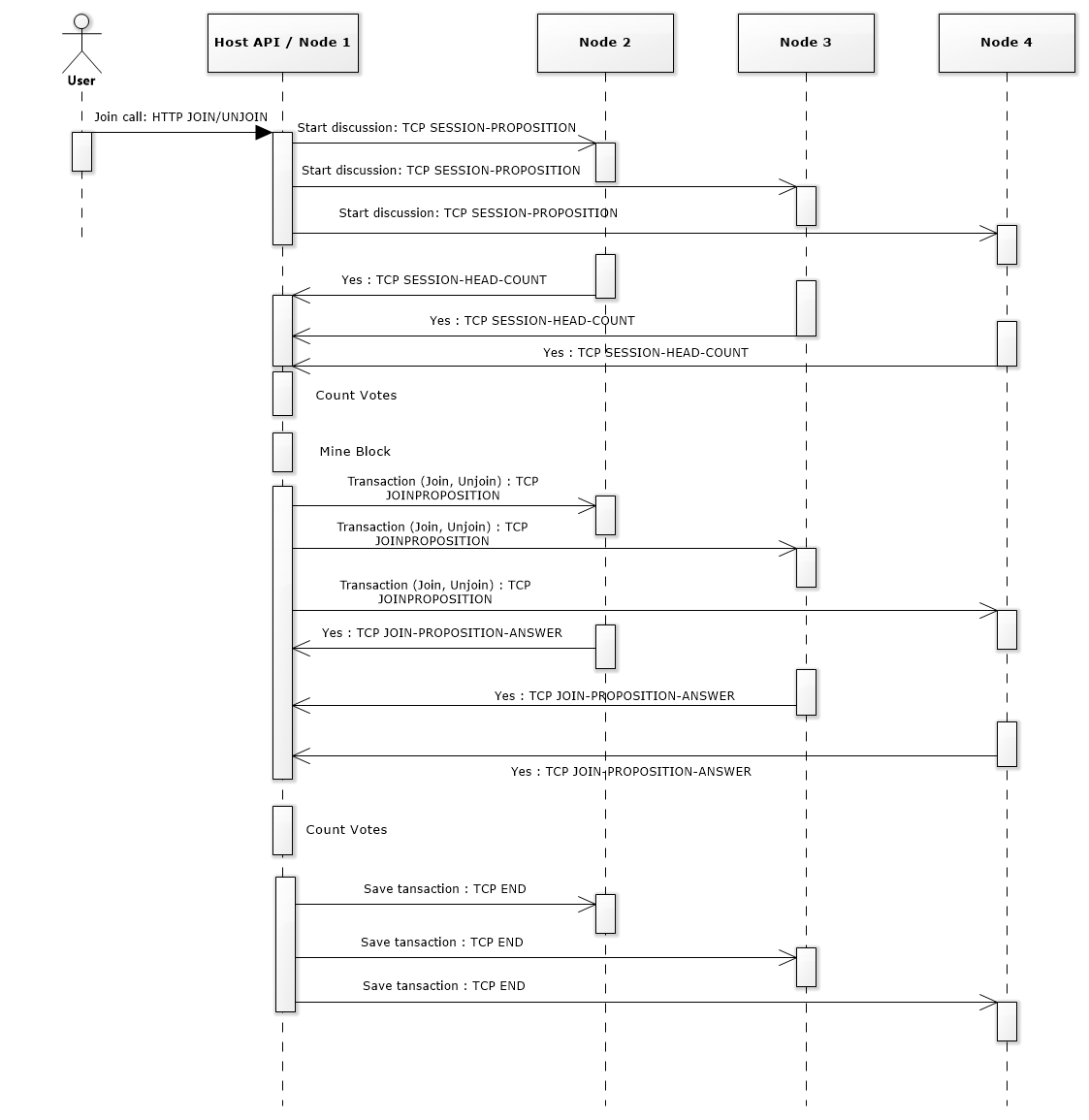
Limits of the programs
We are aware of the following limit to our BlockChain system:
- Discussion queue must be empty when a new node connects. The discussion queue is not tranfered to when a new node connects.
- Our Blockchain has a length of maximum 8.1 blocks if a new node wants to join. As per now, it will send the whole blockchain to the new node but after 8.1 blocks it cannot send the whole chain any longer. (Calculated from the knowlegde that a block is 185 bytes in our system, and with TCP packet max size
- Calls to the discuss queue can not happen at the same time. If calls have a time slot of 15 ms between is should be no problem.
- If something occurs at the exact same time, the business logic becomes very heavy.
More detailed documentation
We have made an elaborate documentation on our Wiki-page.


